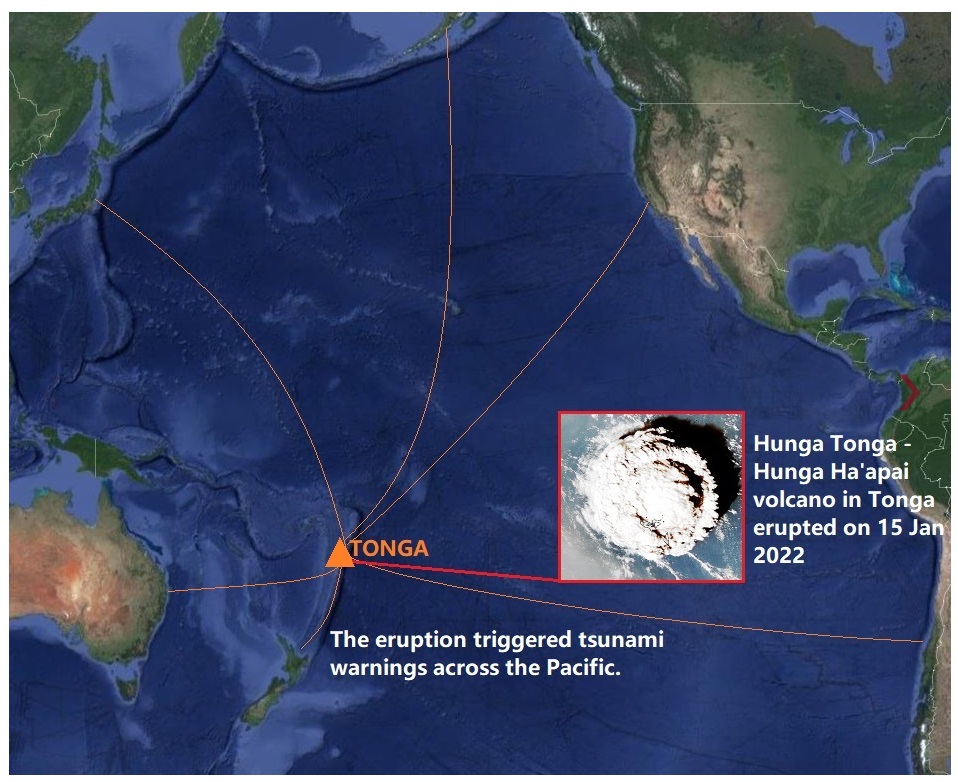
Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano tsunami, 15 January 2022
A large, impulsive eruption at Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano in Tonga causing tsunami on coastlines around the Pacific
Kaikōura tsunami, 14 November 2016
Just like the magnitude 7.8 earthquake that generated it, the tsunami was really complex and had some unusual features.
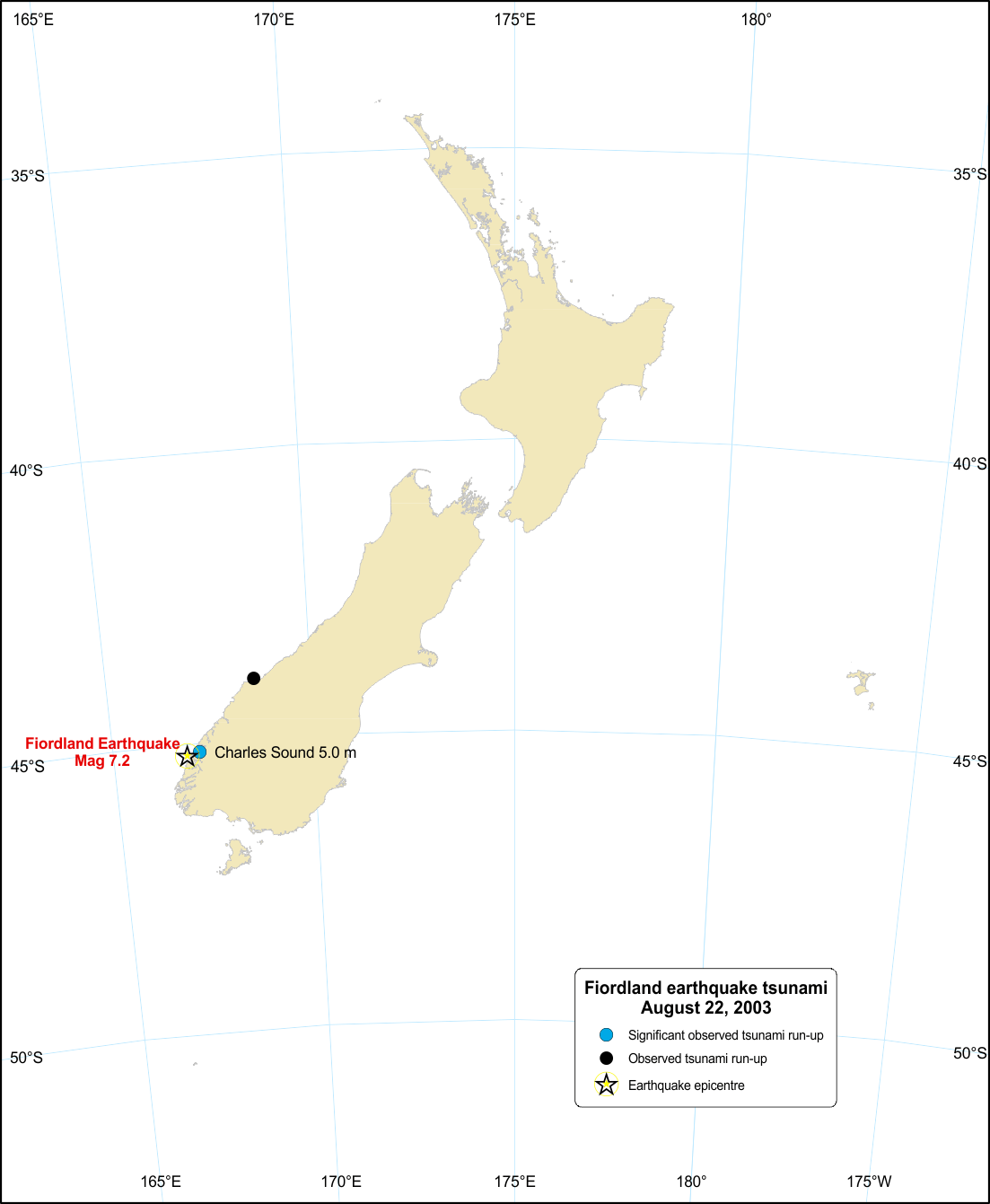
Fiordland tsunami, 22 August 2003
There were two components to this tsunami; one originated from earthquake deformation, the other by a landslide triggered by the earthquake.
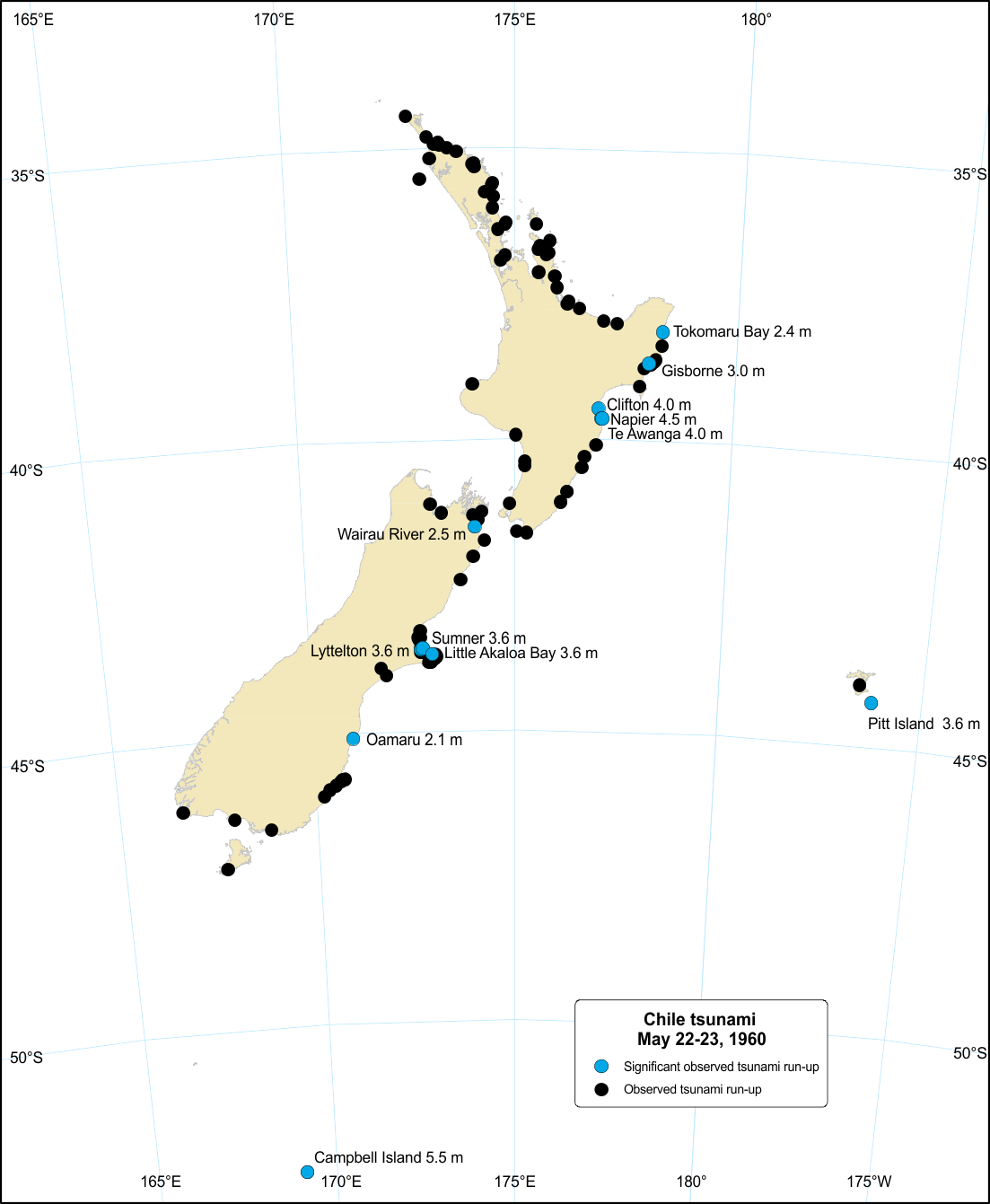
Chile tsunami, 23 May 1960
The largest instrumentally-recorded earthquake in the world caused a tsunami that affected coasts throughout the Pacific Ocean area.
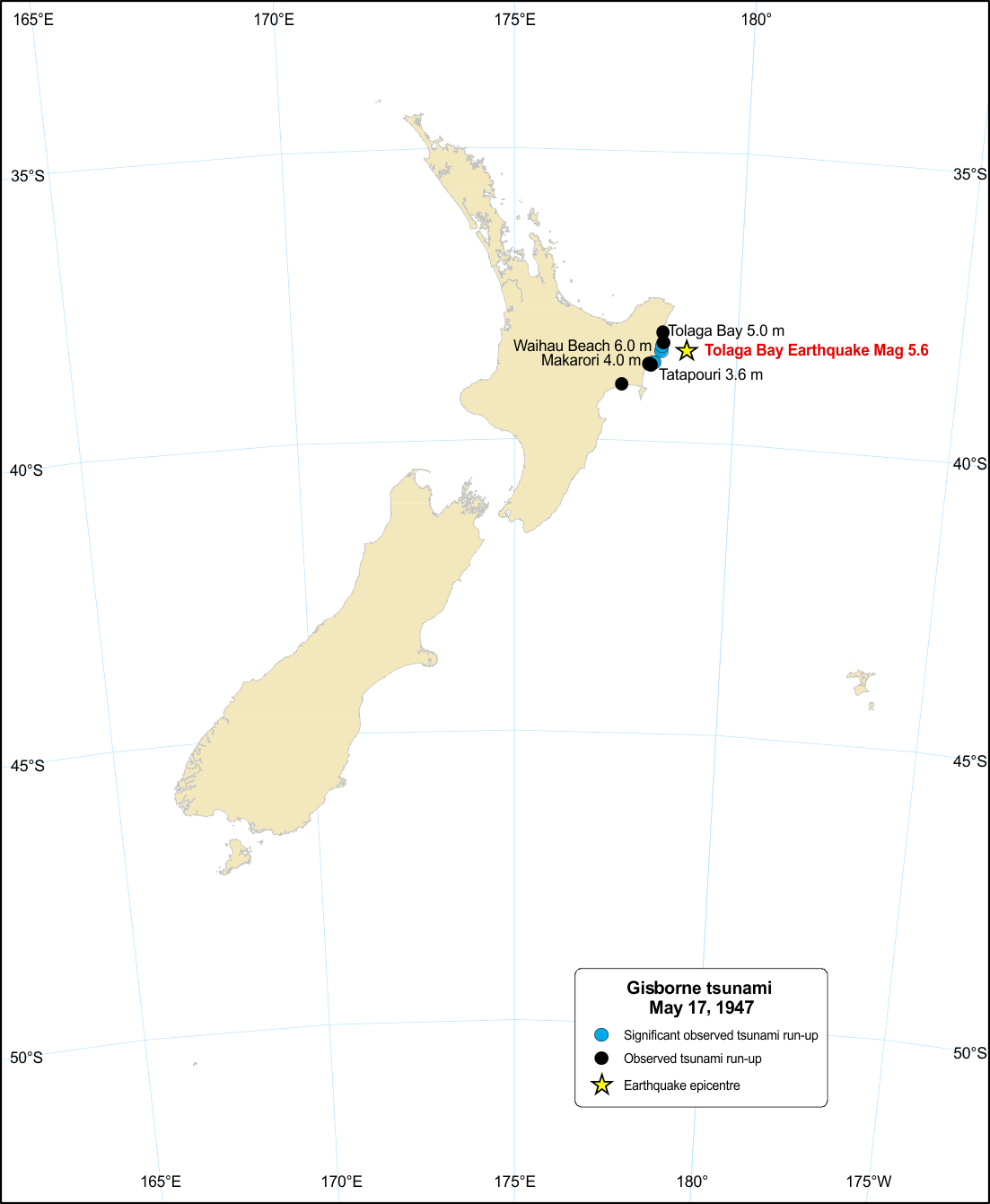
M 6.9 Gisborne, Sat May 17 1947
There were two severe earthquakes off the coast of Gisborne in March and May 1947, each generating large tsunamis in the surrounding area.
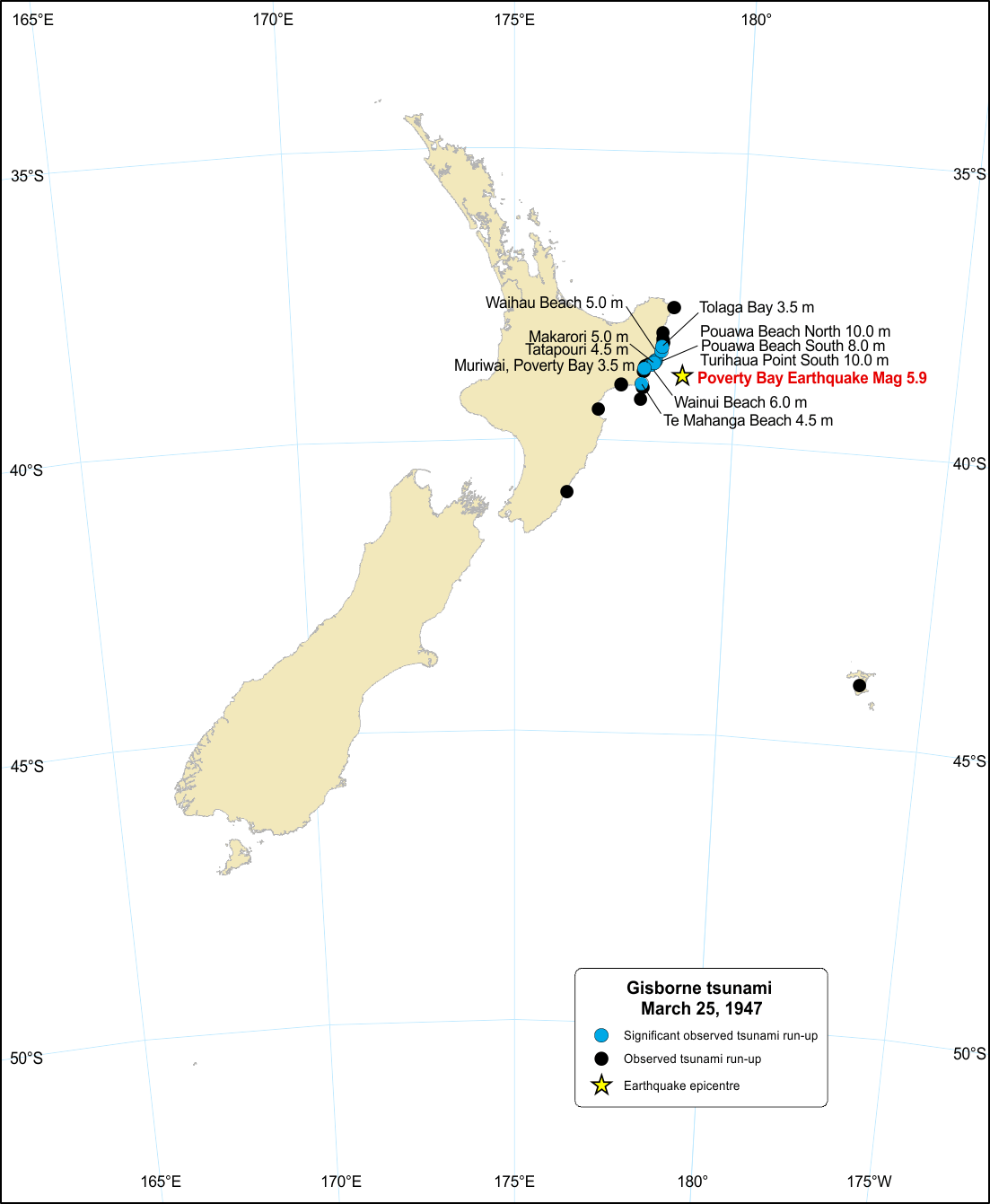
M 7.0 Gisborne, Wed Mar 26 1947
There were two severe earthquakes off the coast of Gisborne in March and May 1947, each generating large tsunamis in the surrounding area. The March tsunami was one of the largest tsunami in New Zealand's historical record.
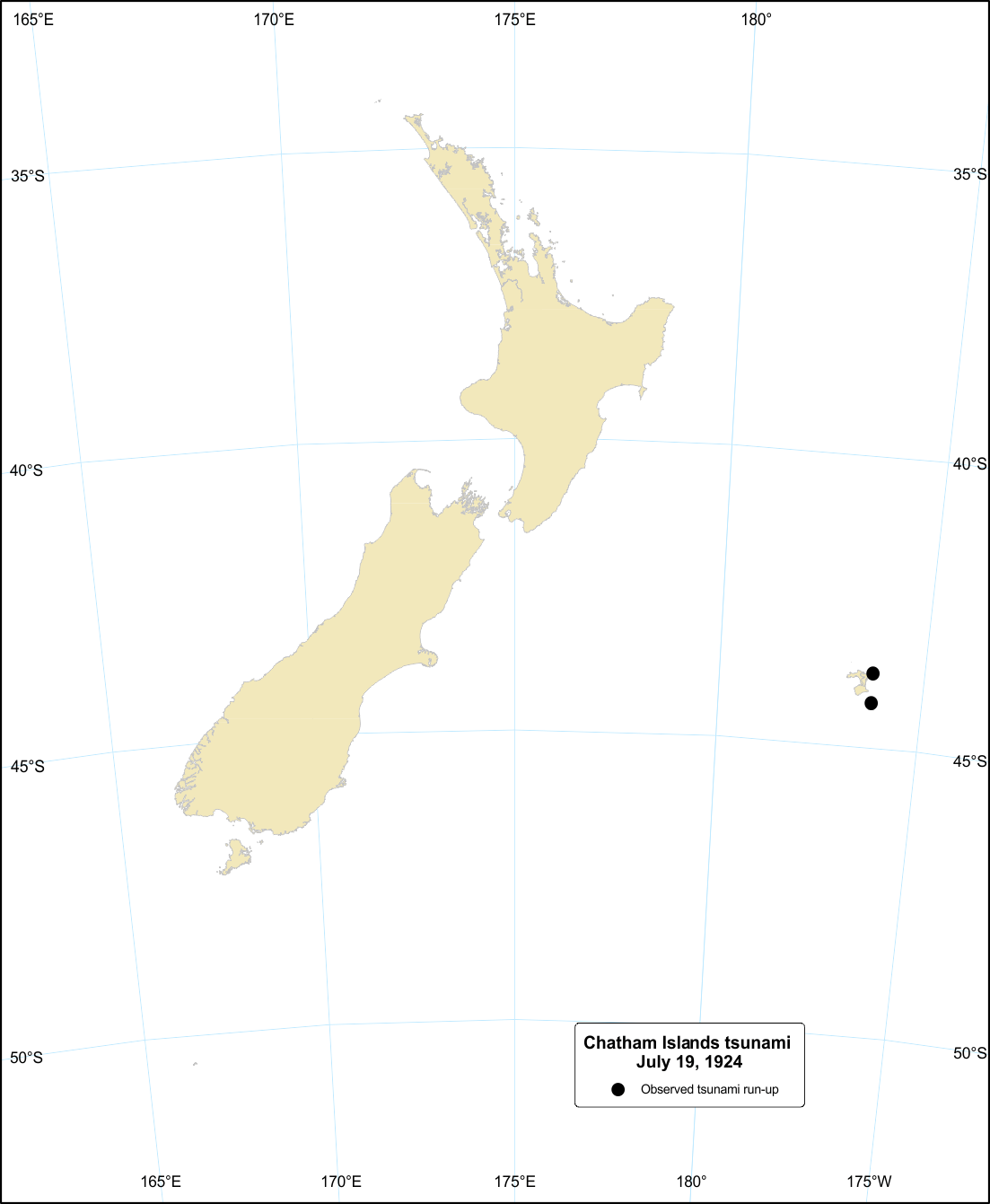
Chatham Islands tsunami, 19 July 1924
The cause of the tsunami observed in Chatham Islands in 1924 is still unknown.
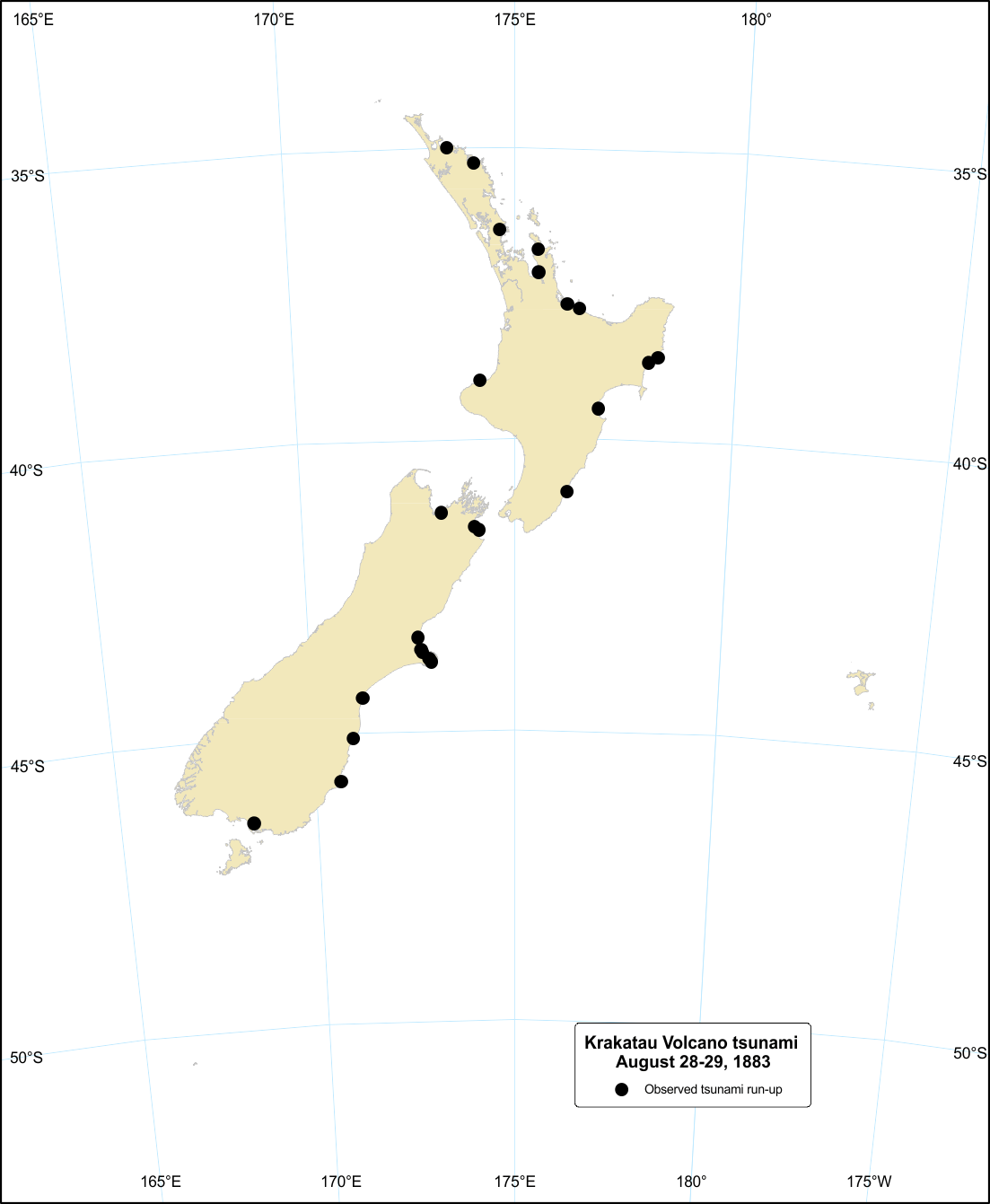
Krakatau Volcano tsunami, 28 to 29 August 1883
This tsunami is the only known example of a New Zealand tsunami generated by a volcano.
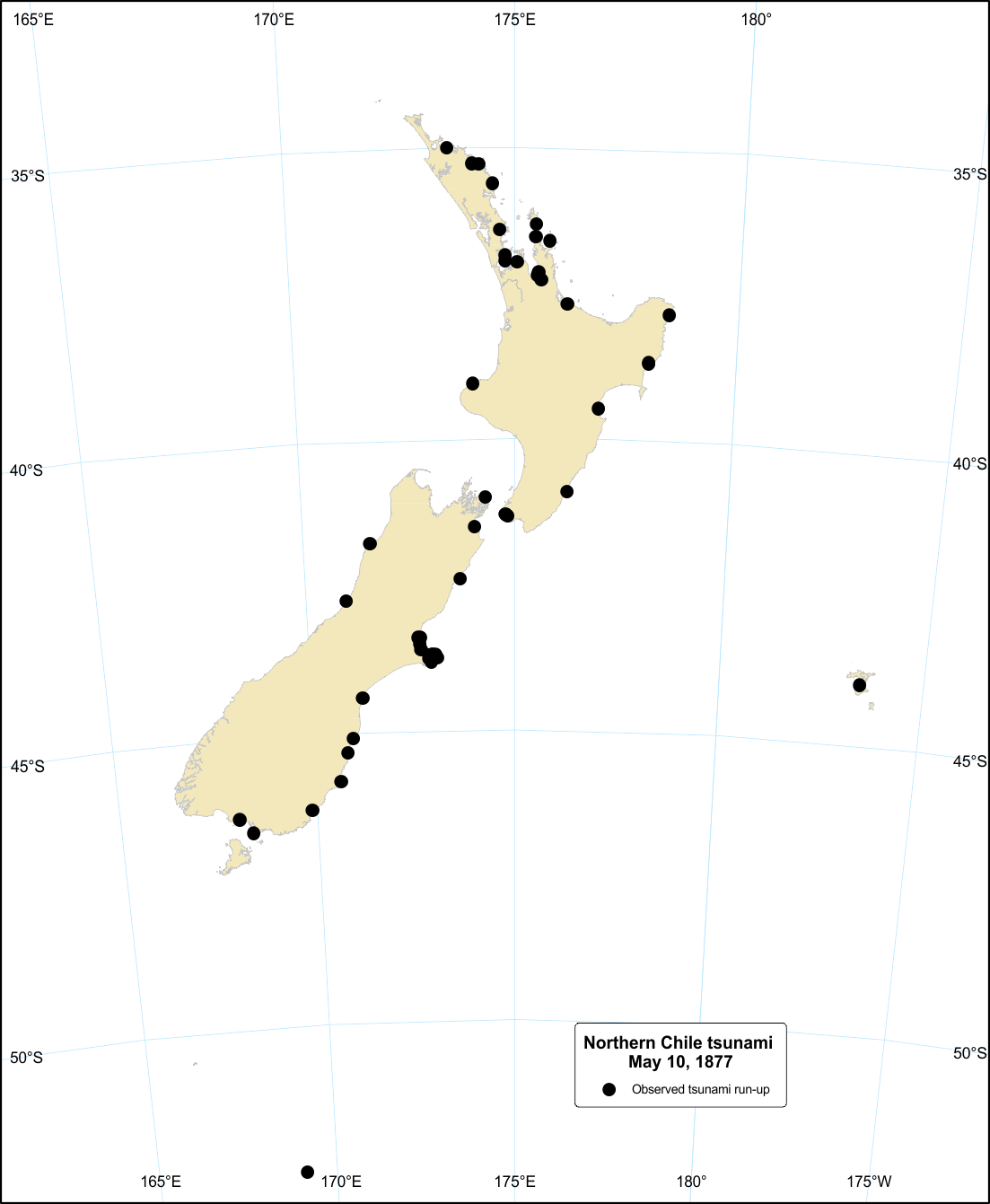
Northern Chile tsunami, 11 May 1877
This tsunami was less pronounced than the 1868 tsunami from Chile, probably because the tides were below Mean Sea Level.
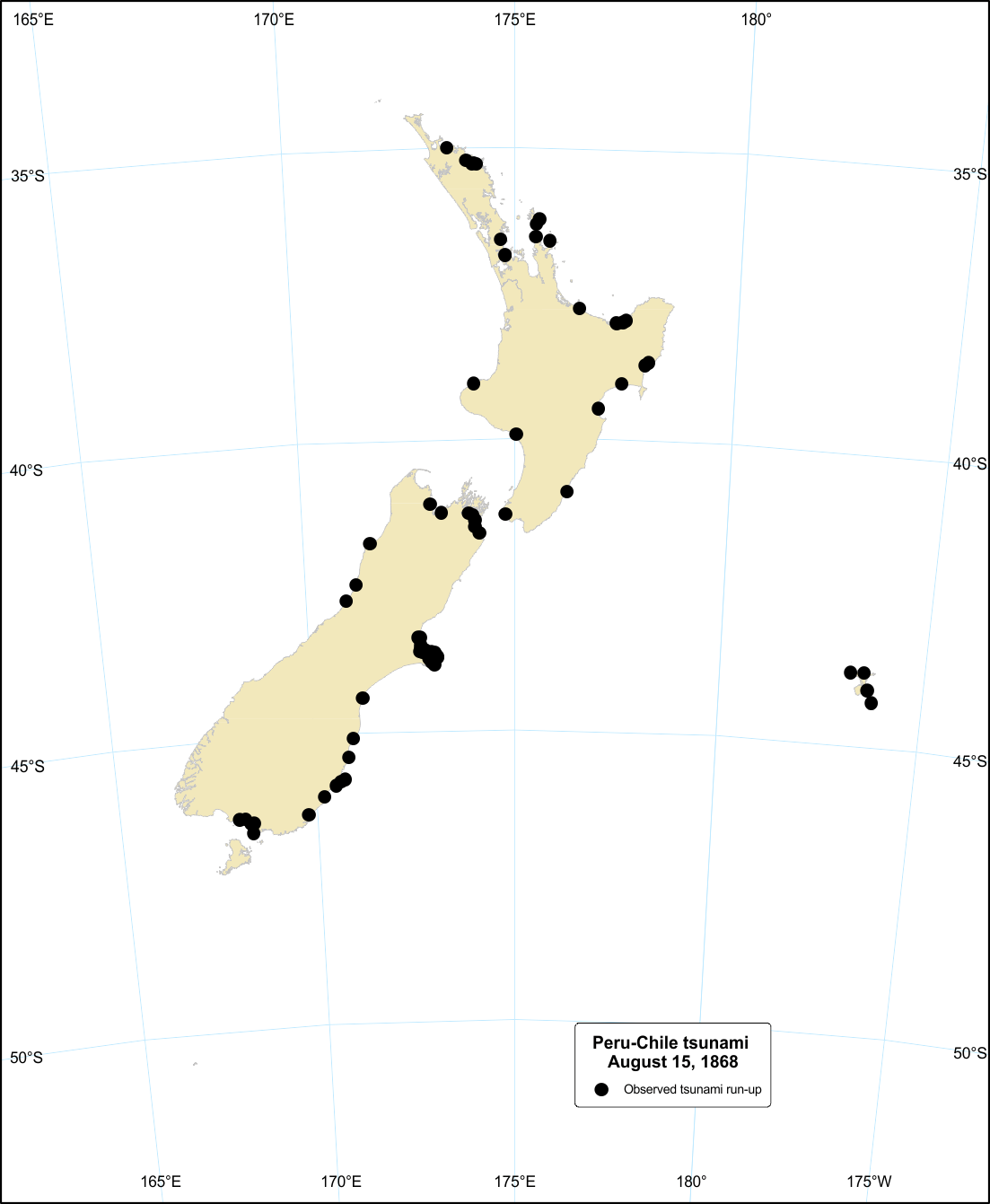
Peru-Chile tsunami, 15 August 1868
This tsunami and earthquake killed thousands of people along the South American Coast.
Wairarapa tsunami, 23 January 1855
This was New Zealand's largest historical locally-generated tsunami